{}
Bronchopleural Fistula
- Etiology of Bronchopleural Fistula (BPF):
- Trauma, empyema/abscess, bullous disease, post lung resection, carcinoma
- Comorbid Disease:
- Chronic obstructive lung disease, malignancy, coronary artery disease, arrhythmias
- Absolute Indication for Lung Separation:
- Protection of healthy lung from soiling
- Ineffective ventilation (with chest tube in place)
- Tension pneumothorax (without chest tube in place)
- Systemic air embolus
- Repeat Thoracotomy Considerations:
- Hemorrhage
- Sepsis, septic shock
- Postoperative analgesia
- Postoperative ICU disposition for positive pressure ventilation (PPV)
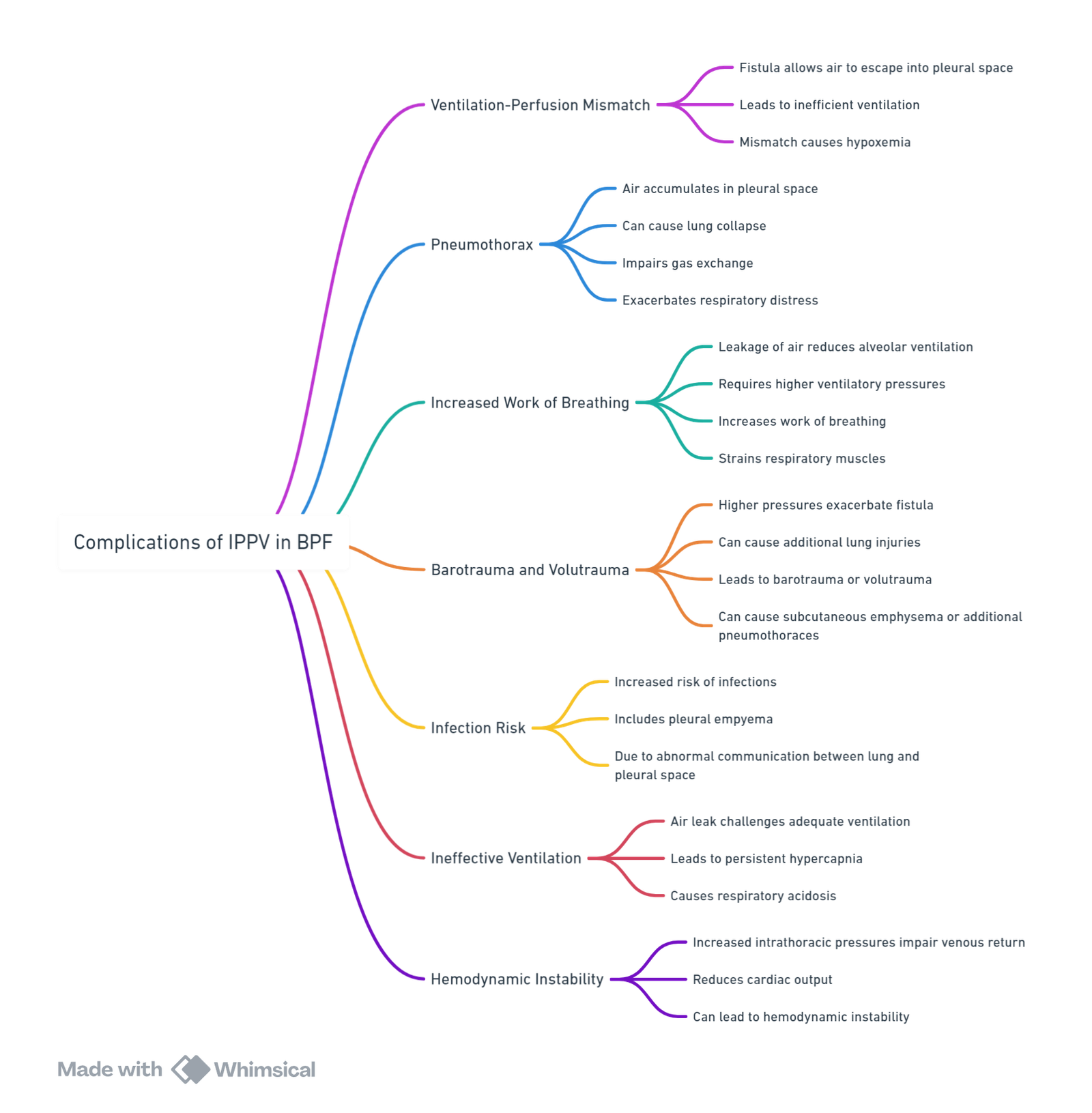
Complications of IPPV in BPF
Size of Fistula Estimation
- Indication via mechanism of injury
- Excessive bubbling in underwater drain
- Respiratory distress & variation in tidal volume (TV) during inspiration and expiration
- Chest X-ray: Lung collapse despite drain insertion
- CT scan: Visualization of fistula size
Approach
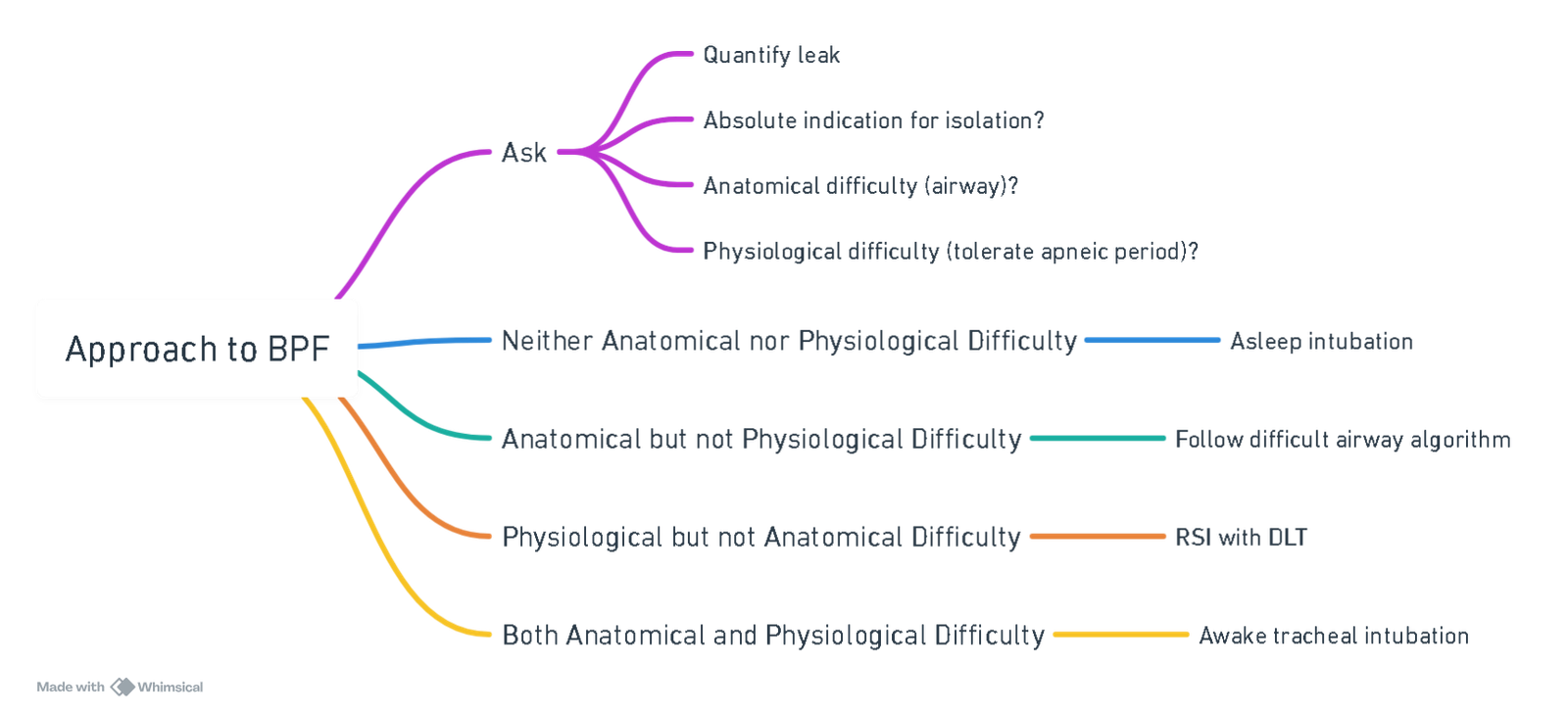
View or edit this diagram in Whimsical.
Goals & Conflicts
- Lung Isolation Prior to PPV:
- Prevent pathophysiological complications
- Challenges: full stomach, difficult airway, hemodynamic instability, limited functional reserve
- Rapid Sequence Lung Isolation Techniques:
- Regional anesthesia
- Awake fibreoptic intubation: single lumen endotracheal tube (ETT) ± bronchial blocker, double lumen ETT prior to general anesthesia (GA)
- Asleep intubation with spontaneous ventilation prior to isolation
- Modified rapid sequence induction (RSI) with no or limited PPV prior to lung isolation
- Double lumen ETT preferred to bronchial blocker for optimal suctioning, ventilation, and isolation
- Need for Resuscitation & Stabilization Prior to OR:
- Fluids, vasopressors, antibiotics, chest tube placement
- Immediate availability of thoracic surgeon for chest tube placement if not in place prior to OR
- Intraoperative Goals:
- Lung protective ventilation
- Restrictive fluid strategy
- Maintenance of normothermia & normal metabolic parameters
- Optimization for Postoperative Extubation:
- Resuscitation
- Bronchial suctioning
- Bronchodilators
- Extubation to BiPAP
Induction
- Small Fistula:
- Conventional induction
- Large Fistula:
- Spontaneous respiration (gas induction or awake intubation)
- Position patient with “fistula side down”
- Double Lumen Tube (DLT):
- More secure but requires patient to be asleep during intubation
- Single Lumen Tube (SLT) & Bronchial Blocker (BB):
- Less secure but allows patient to be awake during intubation
- Alternative Options:
- Thoracic epidural
- Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO)
Ventilation
- Small Fistula:
- Managed with single lumen ETT
- Small tidal volume (TV)
- Increased respiratory rate (RR)
- Elimination or minimization of positive end-expiratory pressure (PEEP)
- Large Fistula:
- May need double lumen ETT
- Ventilation strategies for the lung with the fistula:
- Increased RR and small TV
- Continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) below critical pressure
- High-frequency jet ventilation
Links
- Double lumen and Bronchial blocker
- Respiratory physiology and Thoracic anaesthesia
- Open chest and Empyema
- Lung resection
- Bronchiectasis
References:
- Camargo, A. A. d., Lanza, F. C., Tupinambá, T., & Corso, S. D. (2013). Reproducibility of step tests in patients with bronchiectasis. Brazilian Journal of Physical Therapy, 17(3), 255-262. https://doi.org/10.1590/s1413-35552012005000089
- Salik I, Vashisht R, Sharma S, et al. Bronchopleural Fistula. [Updated 2024 Aug 12]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2024 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK534765/
- Anesthesia Considerations. (2024). Retrieved June 5, 2024, from https://www.anesthesiaconsiderations.com/
Summaries:
Copyright
© 2025 Francois Uys. All Rights Reserved.
id: “608a74fd-efc9-4afe-9ae0-7067e4dae6a4”



