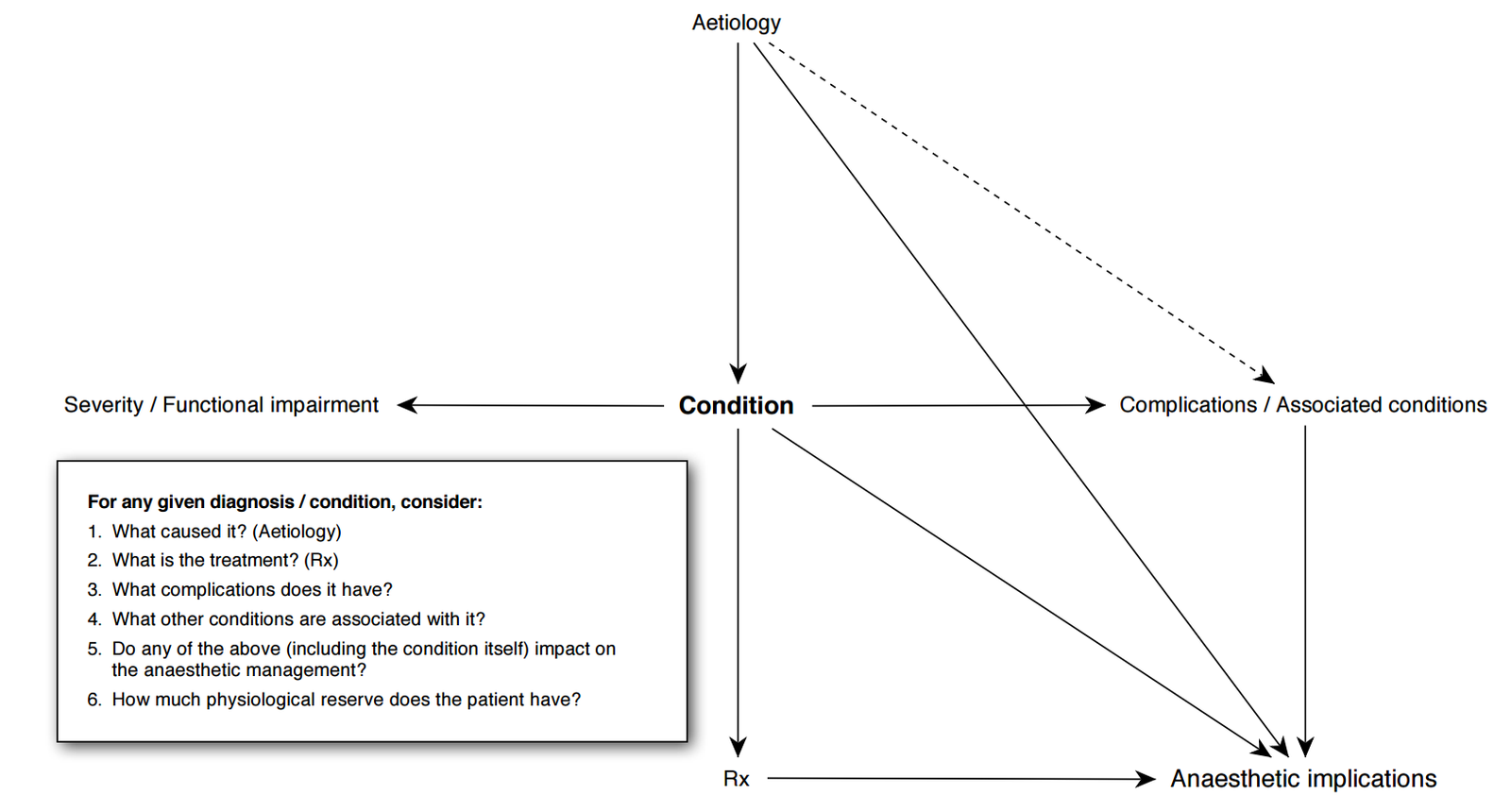
- Approach to Any Condition
- Manual Infusions (TIVA)
- Practical Protocol for TCI Using Different Models
- Red Cross Hospital Sedation Protocol for MRI or Radiotherapy (Children)
- Fibre Optic Protocol
- Ketamine/Magnesium Sulphate/Lidocaine (KLM) Loading and Infusion
- Procedural Sedation
- Epidural Protocols
- Laryngospasm Mix
- PCA Pump Recipes
- Wound Infusion Catheters at GSH
- Helpful Doses and Infusions
- Total Intravenous Anaesthesia (TIVA)
- Malignant Hyperthermia (MH)
- Intralipid 20%
- Noradrenaline
- Adrenaline
- Milrinone
- Clysis
- Sufentanil
- Dexmedetomidine
- Porrill Infusion (KLM)
- Post-op Infusion
- Lidocaine Infusion
- Tranexamic Acid (TXA)
- Neb/Topical Mix
- Spray for Down Peadiatric ETT (Bronchospasm mix)
- Valeron (Tilidine)
- Blood Products
- Calcium Gluconate
- Ketamine – Burns (TIVA)
- Laparoscopic Surgery for Neonates
- Hypoglycemia
- Mannitol
- Hypertonic Saline
- Asthma Management
- Epidural for C/S
- Transfer Checklist
- Opioid-Free Analgesia (OFA)
{}
Approach to Any Condition
Manual Infusions (TIVA)
Anaesthesia
| Drug | Loading Dose (microgram/kg) | Maintenance Infusion (microgram/kg/min) | Maintenance Infusion (microgram/kg/h) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Alfentanil | 50-150 | 0.5-3 | 30-90 |
| Fentanyl | 5-15 | 0.03-0.1 | 1.8-6.0 |
| Sufentanil | 0.5-5 | 0.01-0.05 | 0.6-3.0 |
| Remifentanil | 0.5-1.0 | 0.1-0.4 | 6-24 |
| Ketamine | 1500-2500 | 25-75 | 1500-4500 |
| Propofol | 1000-2000 | 50-150 | 3-9 |
| Midazolam | 50-150 | 0.25-1.5 | 15-90 |
Sedation or Analgesia
| Drug | Loading Dose (microgram/kg) | Maintenance Infusion (microgram/kg/min) | Maintenance Infusion (microgram/kg/h) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Alfentanil | 10-25 | 0.25-1 | 15-60 |
| Fentanyl | 1-3 | 0.01-0.03 | 0.6-1.8 |
| Sufentanil | 0.1-0.5 | 0.005-0.01 | 0.3-0.6 |
| Remifentanil | † | 0.025-0.1 | 1.5-6 |
| Ketamine | 500-1000 | 10-20 | 600-1200 |
| Propofol | 250-1000 | 10-50 | 600-3000 |
| Midazolam | 25-100 | 0.25-1 | 15-60 |
Practical Protocol for TCI Using Different Models
General Principles
- Remifentanil TCI targets:
- Minto ≈ Eleveld (reduce in elderly).
- Eleveld targets are lower than Marsh → Lower than Schnider for propofol during the first 10 min.
- Key point: Titrate to individual patient/procedure
Sedation
- Propofol TCI range: 0.5–2.0 µg/mL.
- Painful parts:
- Occasional pain:
- Alfentanil: 0.25-0.75 mg.
- Remifentanil: 0.2-0.5 µg/kg bolus.
- Continuous or frequent pain:
- Remifentanil infusion: TCI 0.5–2.0 ng/mL.
- Occasional pain:
- Key point: Always titrate for free airway–adequate spontaneous ventilation!
General Anaesthesia
- Start with:
- Propofol sedation and/or remifentanil for sensitivity testing.
- Propofol Induction Targets (TCI):
- Eleveld: 3.0 µg/mL.
- Schnider: 6.0* µg/mL.
- Marsh: 4-5* µg/mL.
- *(For March and Schnider reduce to 3-4 µg/mL after unconsciousness, i.e., after a few minutes.).
- Remifentanil Targets:
- Laryngeal Mask Airway (LMA): 6 ng/mL.
- Endotracheal Tube (ETT): 10 ng/mL.
- Maintenance:
- Propofol 2.5-4 µg/mL.
- Remifentanil as needed (2-15 ng/mL).
Children TIVA Recipe
- Propofol 10mg/ml
- Bolus 3-5mg/kg over 3 min
- Start at 15-10mg/kg/hour for 30 min then 8-10mg/kg/hour
- This is equivalent to 3ug/ml effect site concentration.
- Remifentanil: Draw up solution to 1ug/kg/ml
- Bolus 1-5ug/kg
- Run at 6 ml/hour = 0.1ug/kg/min
- Precedex 4ug/ml
- Bolus: 0.51ug/kg bolus over 10 min
-
- 0.5ug/kg bolus has been shown to lead to faster recovery Use for short cases
-
- Target 0.5ug-1ug/kg/hour
Red Cross Hospital Sedation Protocol for MRI or Radiotherapy (Children)
- Dexmedetomidine
- IVI: 1-2ug/kg bolus over 5 min (lasts between 30-45min)
- Top up: 0.5-1ug/kg
- Nasal: 3-4ug/kg
- IVI: 1-2ug/kg bolus over 5 min (lasts between 30-45min)
- Propofol
- 1-2mg/kg can be added or used as top up sedation
- Or TCI targeting CET 1.8-3.0 (Paedfuser or Eleveld)
- Clonidine (for older children who can actually lie still)
- Used as 5ug/kg oral 1 hour pre-op
- Always enquire if contrast will be required
- IV line will then be required
- Paradoxical reaction about 5 minutes after injection of contrast (unknown aetiology)
- Top up bolus (Dexmed 1ug/kg or propofol 1mg/kg) is usually administered at this time
- Monitoring
- C02 with 20G Jelco at nose, S02 and HR
Fibre Optic Protocol
Awake Fibre Optic Intubation Mix
- Lignocaine Recipe:
- Goal: 4% lignocaine with 20 µg/ml adrenaline
- Components:
- 10% lignocaine
- 1 mg/ml adrenaline (1:1000) diluted to 100 µg/ml
- 2 x 10 ml normal saline ampoules
- Preparation:
- Add 4 ml of 10% lignocaine to a 10 ml syringe
- Add 2 ml of adrenaline mix (100 µg/ml, i.e., 200 µg)
- Fill with saline to a total volume of 10 ml
- Result: 4% lignocaine with 20 µg/ml adrenaline
- Administration:
- Nebulize 5 ml
- Split remaining 5 ml into two 10 ml syringes for spray
- Plan:
- Nebulize in pre-op area
- IVI with clave, give glycopyrrolate
- Consider dexmedetomidine 1ug/kg over 10 min in preop area
- Consider airway blocks (Glossopharyngeal, RLN, superior laryngeal nerve)
- Oxymetazoline drops in each nostril
- Remicaine-covered pus swabs into nasopharynx while setting up/monitoring
- Start sedation ASAP
- Combination of remifentanil 0.05-0.15ug/kg/min (use TIVA not TCI to avoid bolus with TCI) with loading dose of Dexmedetomidine
- Hand Bolus of propofol if required
- If tolerates Remicaine-covered NPA in nostril, proceed with fibre optic intubation
Ketamine/Magnesium Sulphate/Lidocaine (KLM) Loading and Infusion
Option 1
Loading Dose
- Ketamine: 0.2-0.5 mg/kg
- Lidocaine: 1-1.5 mg/kg
- Magnesium Sulfate (MgSO4): 30-50 mg/kg
Maintenance
- In a 50 ml syringe, run at 10 ml/h:
- Lidocaine: 1-1.5 mg/kg
- Ketamine: 0.15 mg/kg
- MgSO4: 15 mg/kg
Example for a 70 kg Man in a 50 ml Syringe for Maintenance @ 10 ml/h:
- Lidocaine: 350 mg (7 mg/ml) 70 ml/hour
- Ketamine: 50 mg (1 mg/ml) 10 mg/hour
- MgSO4: 5 g (100 mg/ml) 1 g/hour
Option 02
-
Components in a 20 ml Syringe:
- Ketamine: 2 mg/ml
- Magnesium: 100 mg/ml
- Lidocaine: 10 mg/ml
-
Doses:
- 2 g Mg
- 40 mg Ketamine
- 200-300 mg Lidocaine
-
Administration:
- Bolus: 0.1 ml/kg over 1 minute
- Infusion: 0.1 ml/kg/h (For every 10 kg, 1 ml/hour)
Calculated Doses
- Lidocaine: 1-1.5 mg/kg
- Ketamine: 0.15 mg/kg
- MgSO4: 15 mg/kg
Procedural Sedation
- Fentanyl Bolus:
- 0.5-1.5 µg/kg
- Typical dose: 50-100 µg (1-2 ml)
Ketafol 10:10 (Almost)
- 20 ml Syringe:
- 18 ml 10 mg/ml propofol (180 mg)
- 2 ml 100 mg/ml ketamine (200 mg)
- 10 ml Syringe:
- 9 ml 10 mg/ml propofol (90 mg)
- 1 ml 100 mg/ml ketamine (100 mg)
- Sedation Dose for 10:10 Ketafol:
- 0.25-0.5 mg/kg
- Example: For 70 kg: 1.5-3.5 ml boluses
ICU Sedation or Transfer Sedation
- Ketafol 10:10 Solution:
- 50 ml Syringe:
- 40 ml 10 mg/ml propofol (400 mg)
- 8 ml 50 mg/ml ketamine (400 mg)
- 2 ml saline
- Total: 8 mg/ml propofol and ketamine
- Initial Bolus for 70 kg: 4-5 ml (500 µg/kg)
- Maintenance Rate for 70 kg: 4-6 ml/hour (10 µg/kg/min)
- 50 ml Syringe:
Ketamine Alone
-
Sedation Dose:
- 4 mg/kg/hour (280 mg/hour)
- Mixture: 200 mg ketamine in a 50 ml syringe with normal saline, run at the patient’s weight
- For 70 kg: 70 ml/hour
-
Double Dose Method:
- Mixture for 8 mg/ml of ketamine
50 ml Syringe with 400 mg ketamine (8 mg/ml)- Run at half the patient’s body weight (35 ml/hour for 70 kg)
- Mixture for 8 mg/ml of ketamine
Ketamine/Midazolam TIVA
- Components:
- Ketamine: 10 mg/ml
- Midazolam: 0.1 mg/kg
- Run at 30-50 ml/hour
Epidural Protocols
Matt O’Neil Recipe
-
Components:
- 10 ml 0.5% Bupivacaine
- 7 ml 2% Lidocaine
- 2 ml Fentanyl
-
Administration:
- Load: 3 ml
- Bolus: 5 ml
- Total volume: 12-15 ml for T10 from L4 epidural
Cary Paediatric Epidural
- Loading Dose:
- 0.25% Bupivacaine 0.2 ml/kg up to 0.8 ml/kg
Labour Epidurals
- Position: Left lateral
- Test Dose:
- 2.5 ml of 2% lignocaine, wait 5 minutes
- Bolus Dose:
- Mix: 5 ml of 0.5% bupivacaine, 4 ml saline, and 50 µg fentanyl (10 ml of 0.25% bupivacaine; 5 µg/ml fentanyl)
- Administer two 4 ml boluses 3 minutes apart
- Measure BP every 5 minutes and test level in 20 minutes (aim T8-T10)
- Infusion:
- Remove 24 ml from a 100 ml saline bag and add 20 ml of 0.5% bupivacaine and 200 µg fentanyl (0.1% Bupivacaine; 2 µg/ml fentanyl)
- Rate: 8-14 ml/hour (start when block is no higher than T8)
- Breakthrough Pain:
- 1.5 ml per segment of 0.25% bupivacaine, divided doses, or 5-10 ml of 0.1% solution with fentanyl 25 µg if near full dilatation
- Top Up for C/S:
- 17 ml 2% lignocaine, 50 µg fentanyl, 1 ml 8.4% sodium bicarbonate, 1 ml 1/10000 adrenaline (diluted to 1 ml)
- Administer 5 ml boluses after test dose
- Total volume: 16-22 ml for effective block to T4
Requirements for Epidural
- 16G or 18G Braun Soft Tip Epidural Kit
- Sterile gown
- Bupivacaine 0.5%
- 100 ml saline
- Fentanyl (from labour ward drug cupboard)
- Saline ampoules
- 10 ml syringe
- 5 ml syringe
- 2 ml syringe
- Lignocaine 2% x 2 (one for test dose, one for skin infiltration)
- Needles: green, pink, and black
- Epidural sterile pack (with gauze, kidney dish, etc.)
- Sterile gloves
- Chlorhexidine bottle
- Tegaderms (large)
- Micropore for strapping
Cardiac Combined Spinal-Epidural (CSE) Recipe
- Intrathecal Injection:
- Hyperbaric bupivacaine: 2.5-5 mg
- Fentanyl: 15-25 µg
- Epidural Boluses:
- Plain 0.5% bupivacaine or 2% lidocaine, 2-3 ml over 15-30 minutes after intrathecal injection
Laryngospasm Mix
- Mixture:
- Lignocaine 2% 1 ml
- Adrenaline 50 µg (0.5 ml)
- Normal Saline 0.5 ml
- Dosage:
- <1 year: 1 ml
-
1 year: 2 ml
PCA Pump Recipes
-
Morphine + Droperidol:
- Morphine: 1 mg/ml (50 mg in 50 ml)
- Droperidol: 25 µg/ml (1.25 mg in 50 ml)
-
Fentanyl + Droperidol:
- Fentanyl: 20 µg/ml (1000 µg in 50 ml)
- Droperidol: 25 µg/ml (1.25 mg in 50 ml)
-
Fentanyl/Ketamine + Droperidol:
- Fentanyl: 20 µg/ml (1000 µg in 50 ml)
- Ketamine: 1 mg/ml (50 mg in 50 ml)
- Droperidol: 25 µg/ml (1.25 mg in 50 ml)
-
Morphine/Ketamine + Droperidol:
- Morphine: 1 mg/ml (50 mg in 50 ml)
- Ketamine: 1 mg/ml (50 mg in 50 ml)
- Droperidol: 25 µg/ml (1.25 mg in 50 ml)
Wound Infusion Catheters at GSH
- Rate: Present on device
- Solution:
- For 0.2% bupivacaine:
- 11 amps of 50 mg in 10 ml in 275 ml
- For 0.2% bupivacaine:
Helpful Doses and Infusions
Total Intravenous Anaesthesia (TIVA)
- Remifentanil:
- Induction: 0.4 µg/kg/min
- Maintenance: 0.2 µg/kg/min
- Propofol:
- Induction: 2 mg/kg (full bolus) and then 10 mg/kg/hr (1 ml/kg/hr)
- Maintenance: 5 mg/kg/hour (0.5 ml/kg/hour)
Malignant Hyperthermia (MH)
- Dantrolene:
- 3 mg/kg, repeat 1 mg every 5 minutes, total 10 mg/kg
Intralipid 20%
- Dosage:
- 1.5 ml/kg (up to 3 doses)
- 15 ml/kg/hr, can increase to 30 ml/kg/hr
Noradrenaline
- Solution:
- 1 mg ampoule
- 4 x ampoules into 200 ml 5% dextrose (20 µg/ml)
Adrenaline
- Solution:
- 60 µg/kg in 50 ml
- 1 ml/hr = 0.02 µg/kg/min
Milrinone
- Solution:
- 1.5 mg/kg into 50 ml
- 1 ml/hr = 0.5 µg/kg/min
Clysis
- Solution:
- 1 amp Plain Marcaine
- 1 amp adrenaline
- 4.4 ml of mix into 200 ml bag
- Max dose: 20 ml/kg
Sufentanil
- Solution:
- 5 µg/ml (250 µg in 50 ml)
- Doses:
- Induction and intubation: 0.2-0.3 ng/ml
- Spontaneous Ventilation (SV): 0.1 ng/ml
- Stop 20 minutes before end
- Decent dose: 1 µg/kg (do not exceed 20 µg in an hour)
Dexmedetomidine
- Solution:
- 200 µg into 50 ml (4 µg/ml)
- Doses:
- 0.2-0.8 µg/kg/hr (spines/awake crani)
- 0.7-1.0 µg/kg/hr (AFOI)
- 0.2-1.4 µg/kg/hr (sedation ICU)
- Model:
- Hannivort: 0.4-0.6 ng/ml
- Normal: 0.1 µg/kg – 1.0 bolus 15 mins
Porrill Infusion (KLM)
- Solution:
- Ketamine: 2 mg/ml (0.4 ml of 100:1)
- Lidocaine: 10 mg/ml (2 ml of 10%)
- MgSO4: 100 mg/ml (2 amps)
- Total:
- 20 ml solution
- Per ml: Lidocaine 10 mg, Ketamine 2 mg, MgSO4 100 mg
- Run at 0.1 ml/kg/hr
Post-op Infusion
- Solution:
- Lidocaine 10 mg/ml
- Ketamine 1 mg/ml
- Doses:
- Initial bolus: Lidocaine 1.5 mg/kg, MgSO4 30 mg/kg, Ketamine 0.2 mg/kg
- Maintenance: Half the rate, stop MgSO4
Lidocaine Infusion
- Solution:
- Bolus: 1.5 mg/kg
- Infusion: 1 mg/kg/hr
Tranexamic Acid (TXA)
- Adults:
- Bolus: 1 g
- Infusion: 1 mg/kg/hr
- Mix: 500 mg in 25 ml total volume (20 mg/ml)
- Paediatrics:
- 500 mg into 50 ml (10 mg/ml)
- Weight/hour: 10 mg/hr
- Bolus dose: 10-30 mg/kg
- Infusion: 10 mg/kg/hr
Neb/Topical Mix
- Solution:
- 2 x 10 ml syringes
- 2 x needles to draw up
- 1 amp 10% lignocaine (5 ml)
- 1 amp adrenaline (1 mg)
- Saline to top up
- Syringe labels
- Preparation:
- Dilute 1 mg adrenaline into 10 ml in one syringe (100 µg/ml)
- Draw up 2 ml of dilute adrenaline and 4 ml lignocaine (400 mg) into another syringe
- Top up with saline to 10 ml (4% lignocaine with 20 µg/ml adrenaline)
- Use 5 ml for nebulization and the rest for spray as you go
Spray for Down Peadiatric ETT (Bronchospasm mix)
- Solution:
- 1 ml 2% lignocaine
- 50 µg adrenaline
- Saline up to 2 ml
- Dosage:
-
1 year: 2 ml
- <1 year: 1 ml
-
Valeron (Tilidine)
- Dosage:
- 1 drop every 2.5 kg (4 drops every 10 kg)
- Frequency: 4-6 hourly
- 1 mg/kg
Blood Products
- Platelets:
- 1 ml/kg increases platelets by 5
- Cryoprecipitate:
- 1 unit (15 ml) per 5 kg or 3 ml/kg increases fibrinogen by 1
- Red Blood Cells:
- 4 ml/kg increases Hb by 1 g/dl
Calcium Gluconate
- Dosage:
- 0.5 ml/kg
Ketamine – Burns (TIVA)
- Dosage:
- Loading: 2 mg/kg
- Infusion: 200 mg in 50 ml (4:1)
- 12 mg/kg/hour for 20 minutes (ml/h = x3 bodyweight)
- 8 mg/kg/hour for 20 minutes (ml/h = x2 bodyweight)
- 4 mg/kg/hour for remainder (ml/h = bodyweight)
Laparoscopic Surgery for Neonates
- Cisatracurium Infusion:
- Loading: 150 µg/kg
- Infusion: 100 µg/kg/hr
Hypoglycemia
- Solution:
- 2.5 ml/kg 10% dextrose slowly
Mannitol
- Dosage:
- 0.25-1 g/kg
Hypertonic Saline
- Dosage:
- 3%: 3-5 ml/kg
- 250 ml over 1/2 hour
Asthma Management
- Nebulizations:
- Salbutamol: 2.5-5 mg every 20-30 minutes
- Fenoterol: 0.5-1 mg
- MDI:
- 2 puffs every 2 minutes up to 10 puffs
- Ipratropium Bromide:
- 250 µg every 20-30 minutes
- Steroids:
- Prednisone/Prednisolone: 1-2 mg/kg PO
- 2-5 years: 20 mg
- More than 5 years: 30-40 mg
- Methylprednisolone: 2 mg/kg 8 hourly IVI
- Dexamethasone: 0.6 mg/kg IVI daily
- Prednisone/Prednisolone: 1-2 mg/kg PO
- IVI Salbutamol:
- 15 µg/kg once over 10 minutes
- Infusion: Loading dose then rate
- IVI Aminophylline:
- Loading dose and infusion with ECG
- MgSO4:
- 30-40 mg/kg
- Ketamine Infusion:
- Leukotriene Receptor Agonists:
- Not used acutely
Epidural for C/S
- Solution:
- 2 ml 8.4% sodium bicarbonate
- 50 µg adrenaline
- 17 ml 2% lignocaine
Transfer Checklist
- Airway: Secure + backup equipment
- Breathing: Method of ventilation/oxygen
- Circulation: IV line
- Disability: Adequate sedation/analgesia, additional drugs you might need
- Exposure: Dignity, warmth, care with adjuncts (e.g., drains)
- Firmly Package: Care with pressure points
- Good Documentation
- Handover
- Team: Porter/sister/anaesthetist
- Monitoring
Opioid-Free Analgesia (OFA)
- Premedication:
- 0.25 µg/kg Dexmedetomidine (max 20 µg) when monitors are applied.
- OFA Mix:
- Dexmedetomidine 50 µg + Ketamine 50 mg + Lidocaine 500 mg diluted to 50 ml with normal saline
- Induction:
- OFA mix 0.1 ml/kg ABW + Propofol to effect + Rocuronium
- Dexamethasone 10 mg
- MgSO4 40 mg/kg ABW
- Maintenance:
- OFA mix 0.1 ml/kg ABW/hr infusion + Propofol infusion or volatile
- Repeat induction bolus if patient remains tachycardic before skin incision
- Additional 25 mg Ketamine before skin incision if needed
- Pre-End of Surgery:
- Decrease OFA mix to 0.05 ml/kg ABW/hr 15 minutes before end
- Post-op:
- Continue OFA mix at 0.05 ml/kg ABW/hr
- Paracetamol and NSAID
Alternative Option:
- Fentanyl 200 µg
- Infusion of Ketamine: 0.2 mg/kg ABW loading dose and 0.1 mg/kg ABW/hr
- Lidocaine: 1.5 mg loading dose and 1 mg/kg ABW/hr
- Remifentanil: 0.1-0.15 µg/kg ABW/min
- Paracetamol: 2 g
- Parecoxib: 40 mg (when not contraindicated)
- Dexamethasone: 8 mg
- Skin infiltration with Bupivacaine prior to port placement
- MgSO4 can be used when sugammadex is available to reverse rocuronium
Conversion Factors
- mmHg to cmH2O:
- 1 cmH2O = 0.74 mmHg
- 1 mmHg = 1.36 cmH2O
Weight Calculation
Total Body Weight (TBW)
The actual weight of the individual.
Lean Body Weight (LBW)
Fat-free mass, used for dosing in certain medical contexts. In the obese, it exceeds Ideal Body Weight and plateaus at:
- Approximately 100 kg for men
- Approximately 70 kg for women
Ideal Body Weight (IBW)
Devine Formula
- Male: 50 kg + 2.3 kg x (height in inches – 60)
- Female: 45 kg + 2.3 kg x (height in inches – 60)
Note: 1 cm = 0.4 inches
Broca Formula
- Men: Height in cm minus 100
- Women: Height in cm minus 105
Adjusted Body Weight (ABW)
Used when TBW is more than 30% above IBW:
- Formula: IBW + 0.4 (TBW – IBW)
Naloxone Infusion Protocol
Naloxone Dosing and Administration
Adult Dose
- IV Bolus: 400-2000 micrograms given by slow IV injection (over 3-5 minutes), repeated at intervals of 2 to 3 minutes, up to 10mg. If a total of 10mg is given with no satisfactory response, then the diagnosis should be questioned.
IV Infusion (Unlicensed Concentration)
- The initial hourly rate for infusion (second column) is set at 60% of the bolus needed to obtain a response and may be adjusted according to clinical response.
| Initial Bolus Dose Giving Response | Initial Hourly Rate of Infusion | Volume per Hour (of 200 micrograms/mL solution) |
|---|---|---|
| 400 micrograms | 240 micrograms/hour | 1.2 mL/hour |
| 600 micrograms | 360 micrograms/hour | 1.8 mL/hour |
| 800 micrograms | 480 micrograms/hour | 2.4 mL/hour |
| 1000 micrograms | 600 micrograms/hour | 3.0 mL/hour |
| 1200 micrograms | 720 micrograms/hour | 3.6 mL/hour |
| 1400 micrograms | 840 micrograms/hour | 4.2 mL/hour |
| 1600 micrograms | 960 micrograms/hour | 4.8 mL/hour |
| 1800 micrograms | 1080 micrograms/hour | 5.4 mL/hour |
| 2000 micrograms | 1200 micrograms/hour | 6.0 mL/hour |
Presentation: Naloxone is stocked at RBCH in 400 micrograms/mL injections and 800 micrograms/2mL Min-I-jets.
Links
Summaries:
Copyright
© 2025 Francois Uys. All Rights Reserved.
id: “05e5c21a-a42e-4701-bc68-461ccd026d9e”



