{}
Whole Lung Lavage
Definition
Whole lung lavage is a therapeutic procedure that involves the irrigation of the lung and bronchial tree. It is primarily used to treat conditions such as:
- Alveolar proteinosis
- Radioactive dust inhalation
- Cystic fibrosis
- Bronchiectasis
- Asthmatic bronchitis
The procedure is performed under general anesthesia using a double-lumen endotracheal tube (DLT) to allow for ventilation of one lung while the other lung is treated with lavage fluid.
Approach
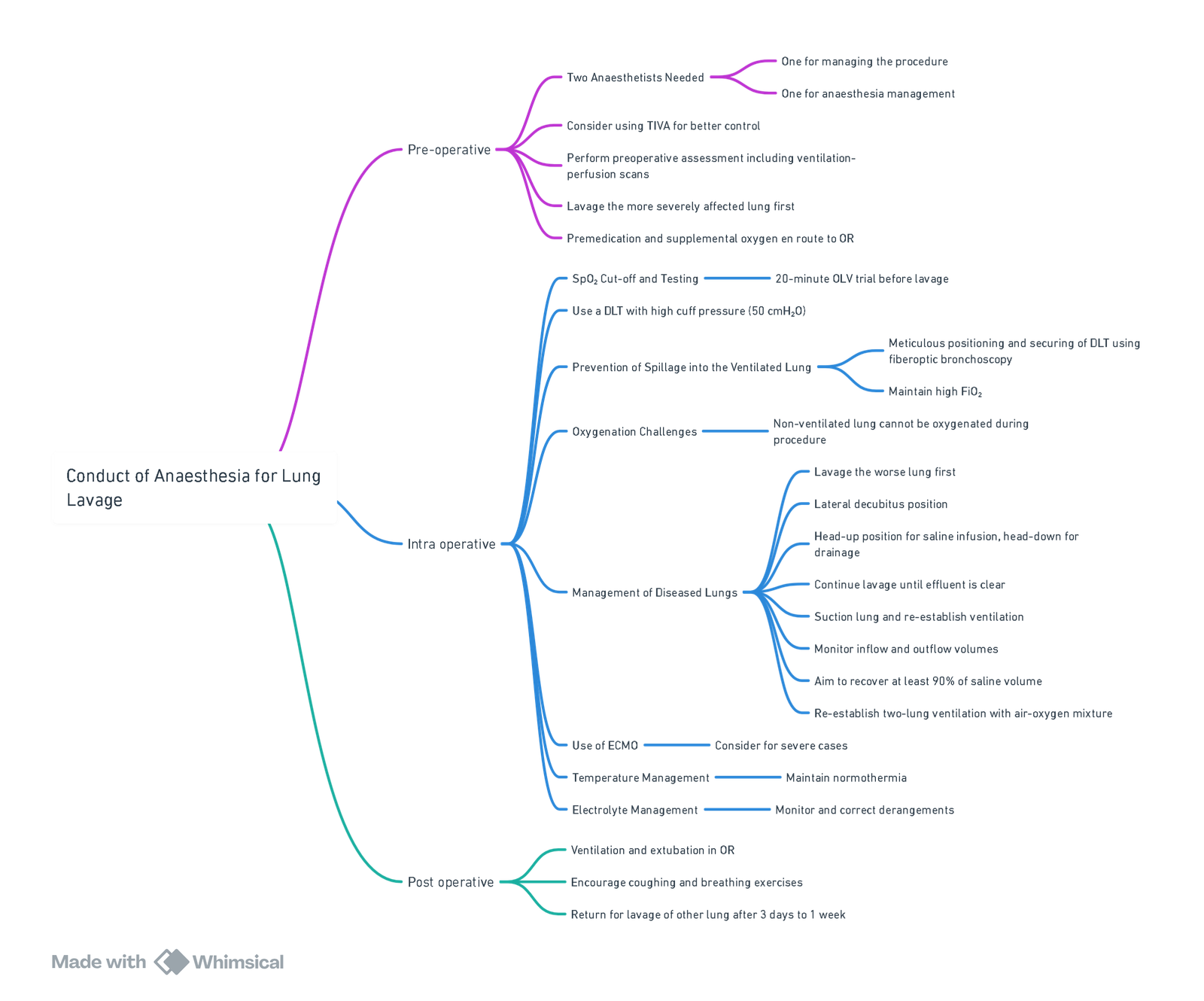
View or edit this diagram in Whimsical.
Complications
-
Spillage of Lavage Fluid:
- Can occur from the treated lung to the ventilated lung.
- Managed by stopping lavage and ensuring functional separation of the lungs before continuing.
- Use a stethoscope over the ventilated lung to check for rales indicating leakage.
- Spillage can cause profound hypoxemia, possibly necessitating termination of the procedure and maintaining two-lung ventilation with oxygen and PEEP.
-
Hypoxemia:
- During fluid instillation into the dependent lung, oxygenation may improve due to increased intra-alveolar pressure diverting blood flow to the ventilated lung.
- Hypoxemia may occur when fluid is drained from the dependent lung.
- Severe hypoxemia during right lung lavage can be mitigated by inflating a balloon-tipped catheter in the right main pulmonary artery to minimize blood flow to the non-ventilated lung during drainage. This technique carries a risk of pulmonary artery rupture and is reserved for high-risk patients.
Limitations
- The size limitations of available DLTs preclude their use in patients weighing less than 40 kg.
- In such cases, cardiopulmonary bypass may be required to provide oxygenation during lavage.
Links
- One lung Ventilation and VATS
- Double lumen and Bronchial blocker
- Open chest and Empyema
- Long volume reduction surgery
References:
- Pandit A, Gupta N, Madan K, Bharti SJ, Kumar V. Anaesthetic considerations for whole lung lavage for pulmonary alveolar proteinosis. Ghana Med J. 2019 Sep;53(3):248-251. doi: 10.4314/gmj.v53i3.9. PMID: 31741497; PMCID: PMC6842735.
Summaries:
Copyright
© 2025 Francois Uys. All Rights Reserved.
id: “6475e857-9cb9-4b3d-bec5-f25daaed21fe”



